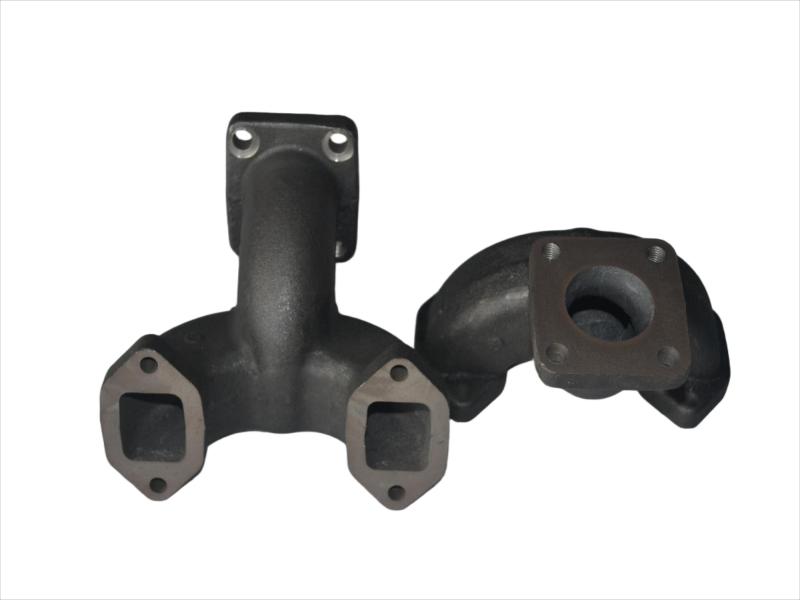
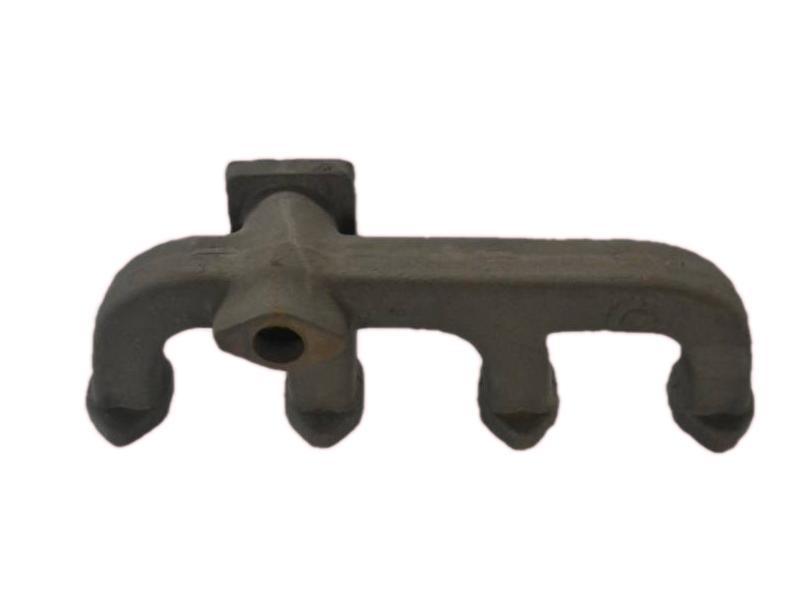
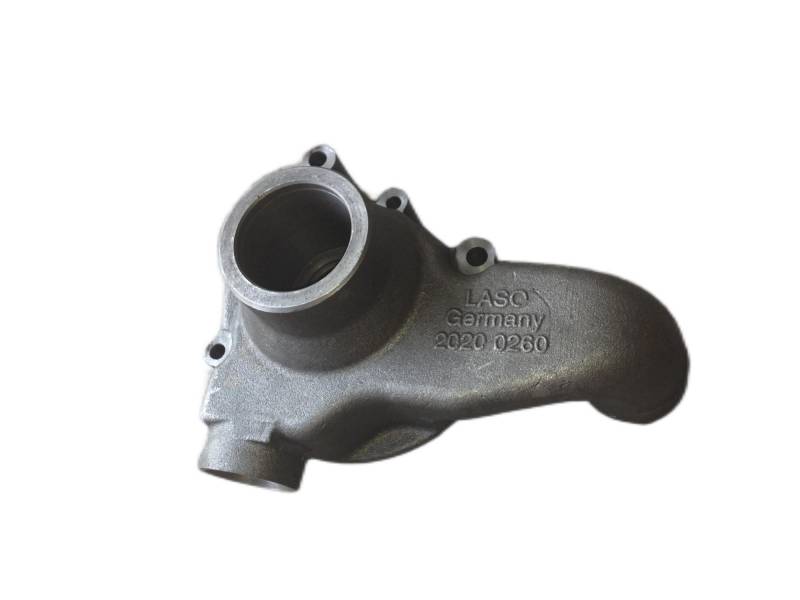
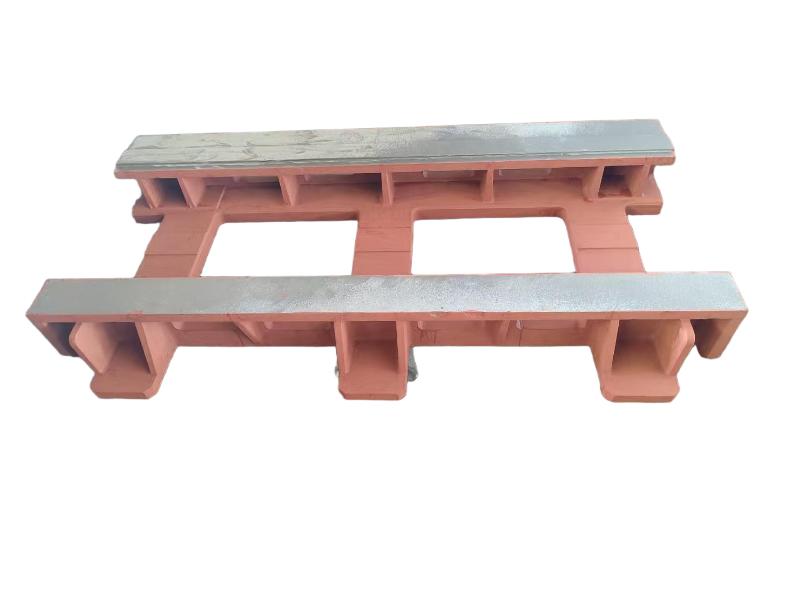
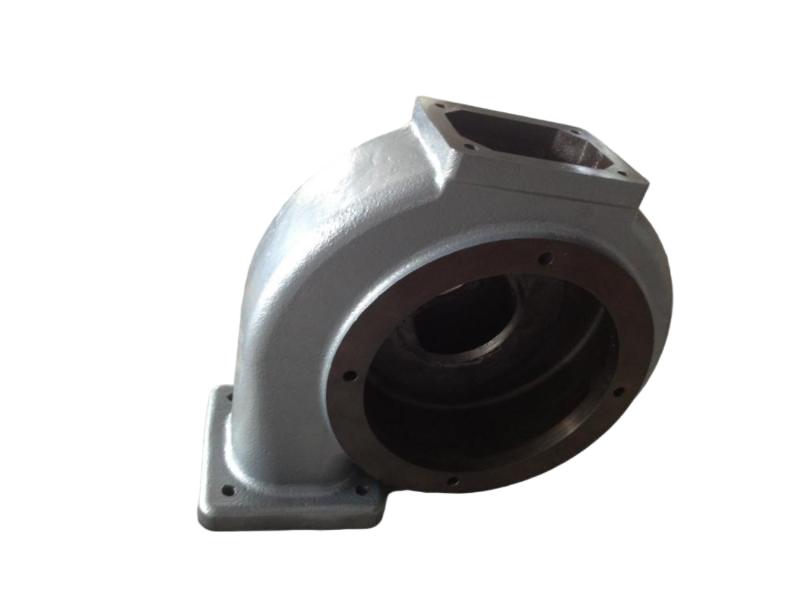
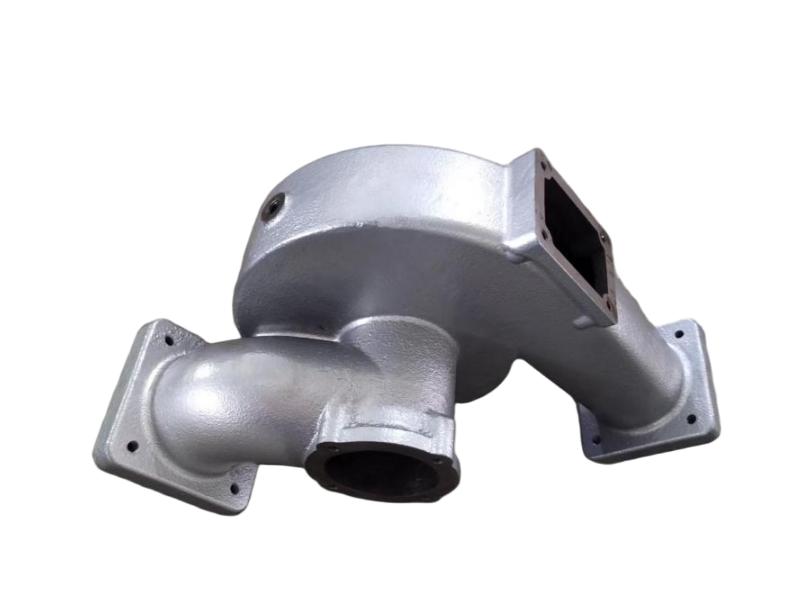
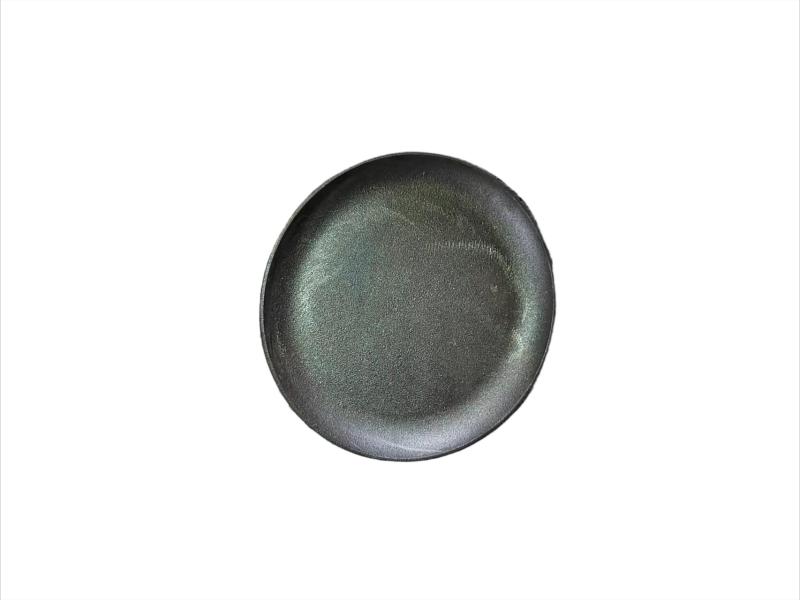
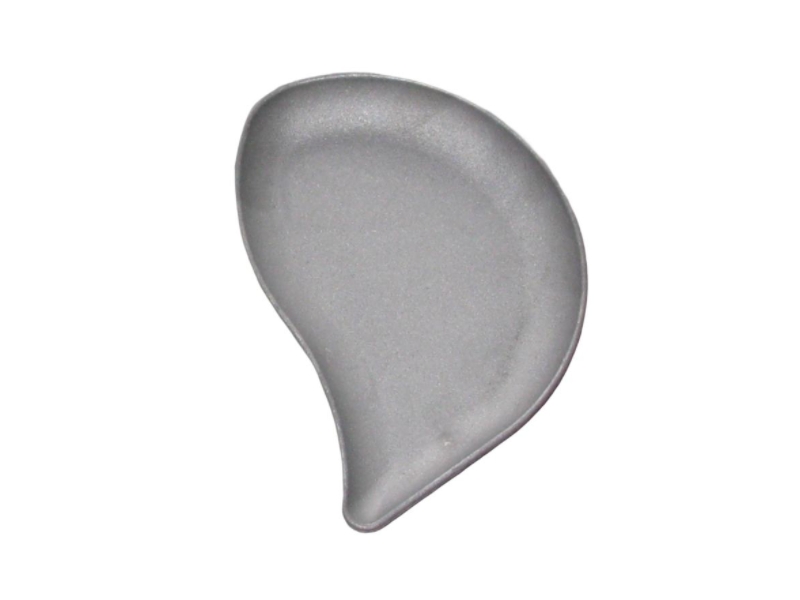
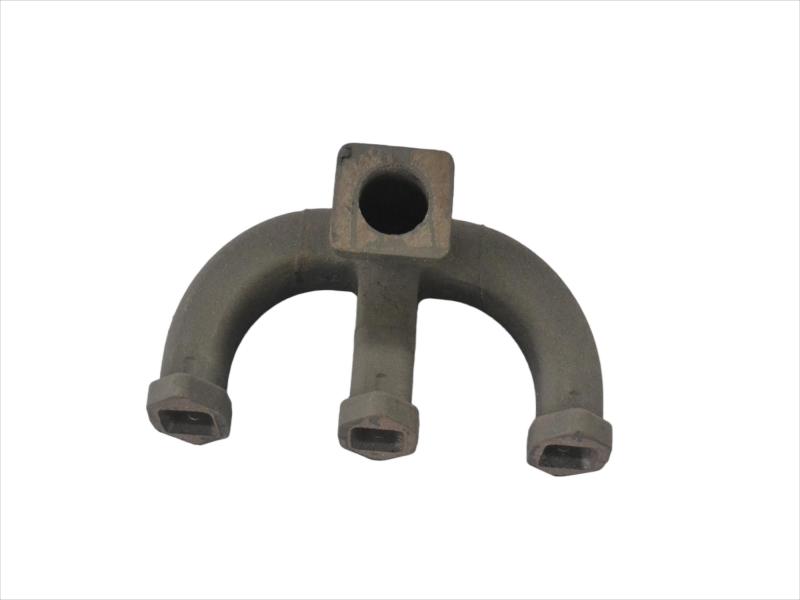
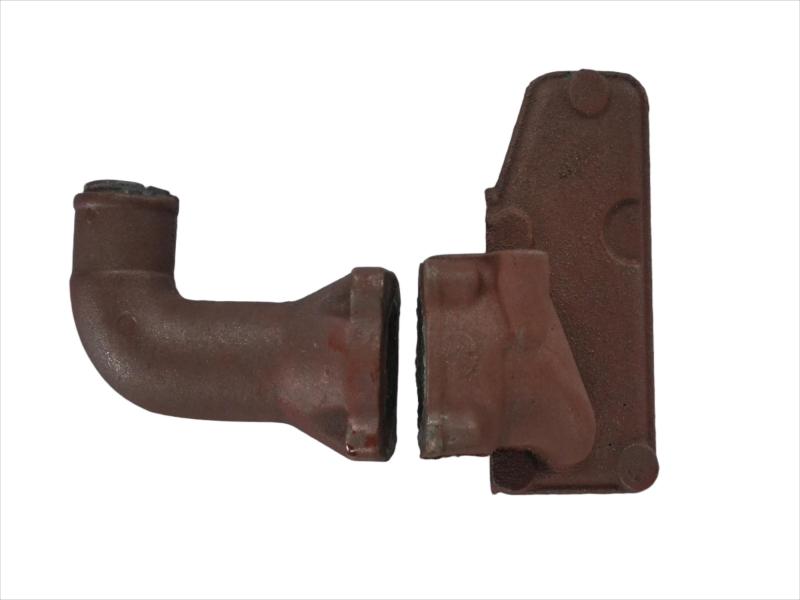
The exhaust manifold is a component of a vehicle's engine that collects exhaust gases from the cylinders and directs them to the exhaust system. It's the first part of the exhaust system, connecting directly to the engine's exhaust ports. The manifold then funnels these gases into the catalytic converter and the rest of the exhaust system.
Hengchang is a OEM exhaust Pipe manufacturer. We have produced lots of grey cast Iron casting exhaust manifold pipe for diesel engine. Gray iron, or grey cast iron, is a type of cast iron that has a graphite microstructure. It is named after the gray color of the fracture it forms, which is due to the presence of graphite. It is the most common cast iron and the most widely used cast material based on weight.
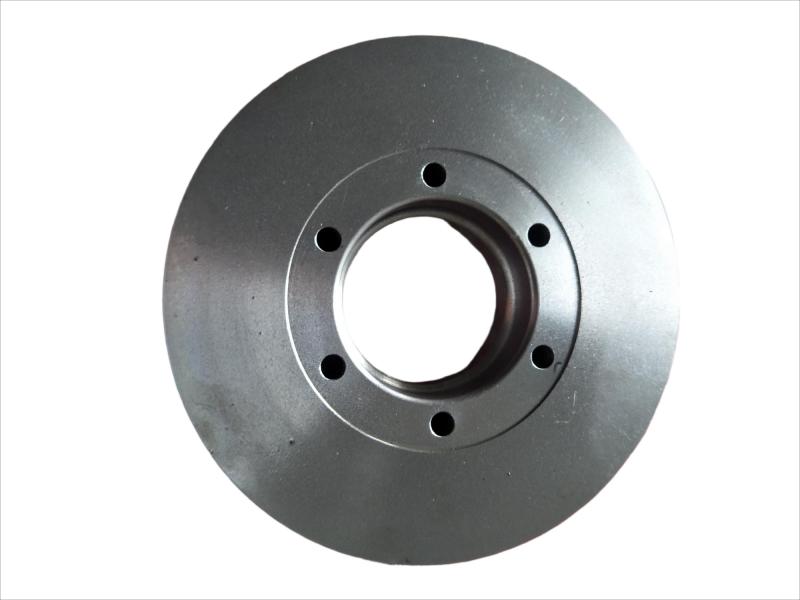
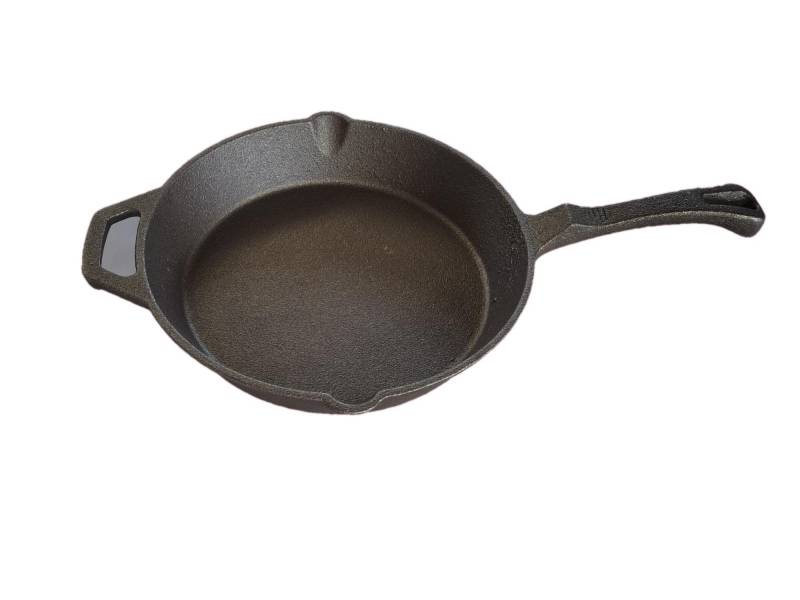
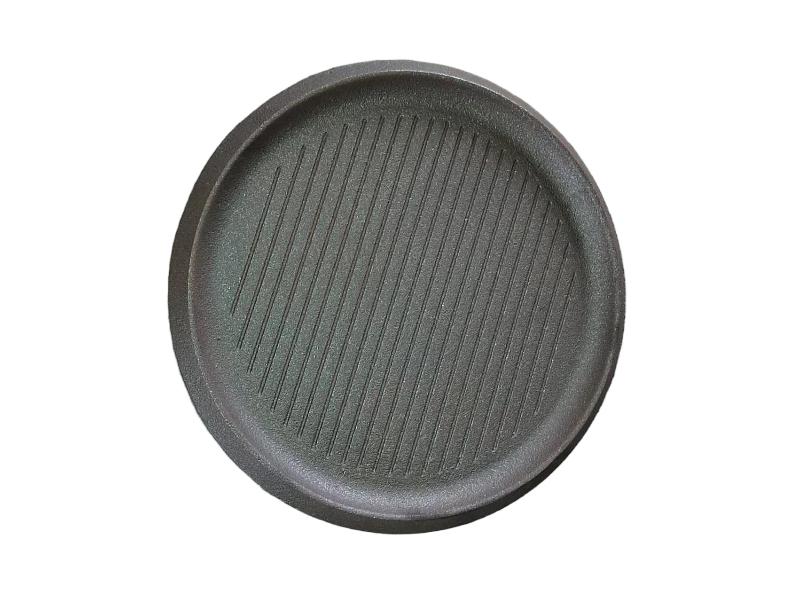
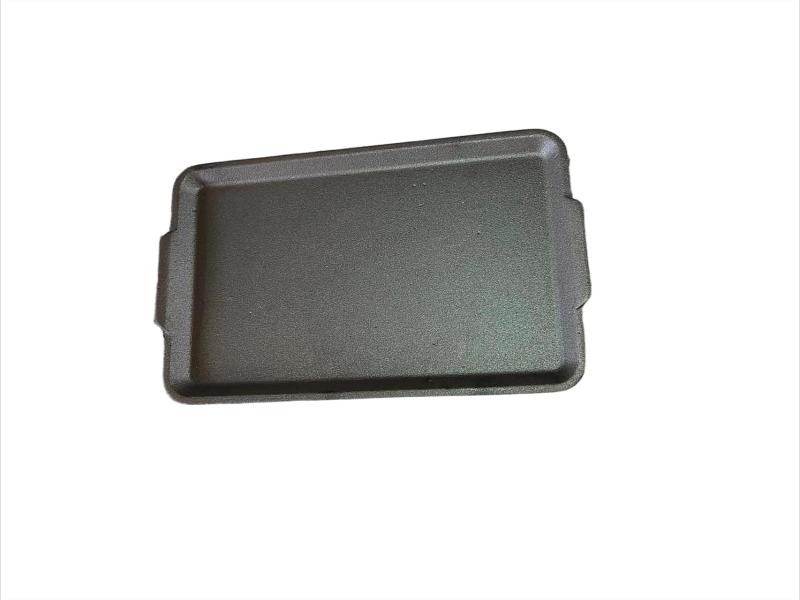
It is used for housings where the stiffness of the component is more important than its tensile strength, such as exhaust manifold, internal combustion engine cylinder blocks, pump housings, valve bodies, electrical boxes, and decorative casting. Grey cast iron's high thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity are often exploited to make cast iron cookware and disc brake and rotors.
| Production Line Capabilities |
1.Vacuum Casting Line: Enables large-batch production and smooth surface medium parts

2.Resin Sand Casting Line: Delivers big complex geometries, but small quantity

3.Clay Sand Casting Line: Enables large-batch production small part and smooth surface medium parts

4.Medium-frequency Induction Furnace: Make sure uniform melting and stable quality

The Structure of Grey Iron
A typical chemical composition to obtain a graphitic microstructure is 2.5 to 4.0% carbon and 1 to 3% silicon by weight. Graphite may occupy 6 to 10% of the volume of grey iron. Silicon is important for making grey iron as opposed to white cast iron, because silicon is a graphite stabilizing element in cast iron, which means it helps the alloy produce graphite instead of iron carbides; at 3% silicon almost no carbon is held in chemical form as iron carbide. Another factor affecting graphitization is the solidification rate; the slower the rate, the greater the time for the carbon to diffuse and accumulate into graphite. A moderate cooling rate forms a more pearlitic matrix, while a fast cooling rate forms a more ferritic matrix. To achieve a fully ferritic matrix the alloy must be annealed. Rapid cooling partly or completely suppresses graphitization and leads to the formation of cementite, which is called white iron.
The graphite takes on the shape of a three-dimensional flake. In two dimensions, as a polished surface, the graphite flakes appear as fine lines. The graphite has no appreciable strength, so they can be treated as voids. The tips of the flakes act as preexisting notches at which stresses concentrate and it therefore behaves in a brittle manner. The presence of graphite flakes makes the grey iron easily machinable as they tend to crack easily across the graphite flakes. Grey iron also has very good damping capacity and hence it is often used as the base for machine tool mountings.
Advantages and disadvantages of Grey Iron
Gray iron is a common engineering alloy because of its relatively low cost and good machineablity , which results from the graphite lubricating the cut and breaking up the chips. It also has good galling and wear resistance because the graphite flakes self lubricate. The graphite also gives gray iron an excellent damping capacity because it absorbs the energy and converts it into heat.Grey iron cannot be worked (forged, extruded, rolled etc.) even at temperature.











































 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported