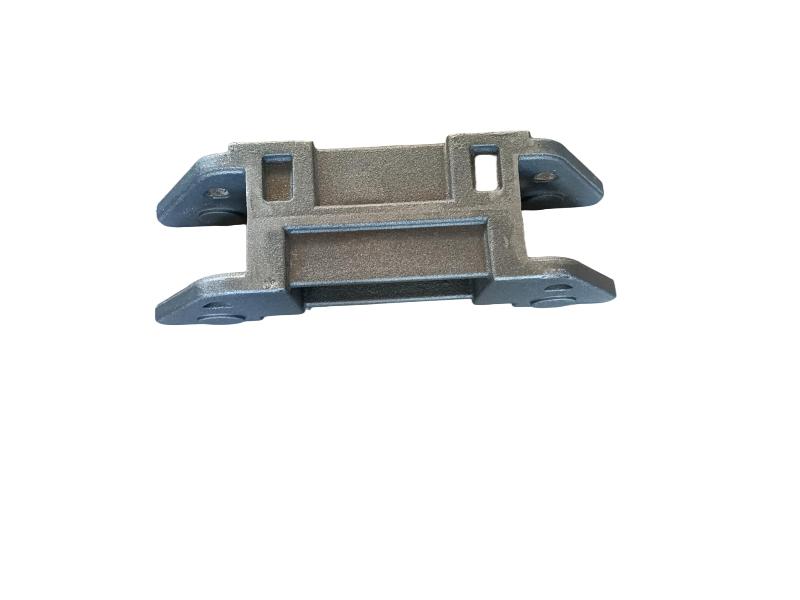
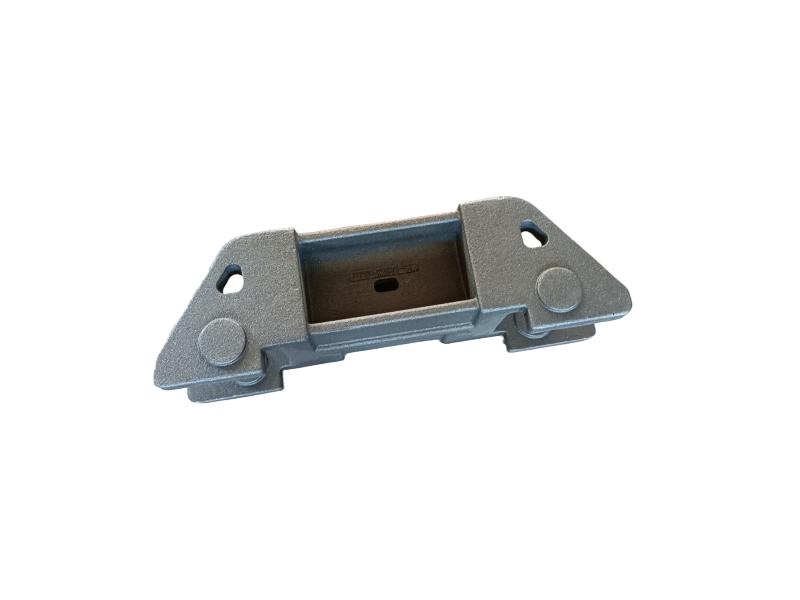
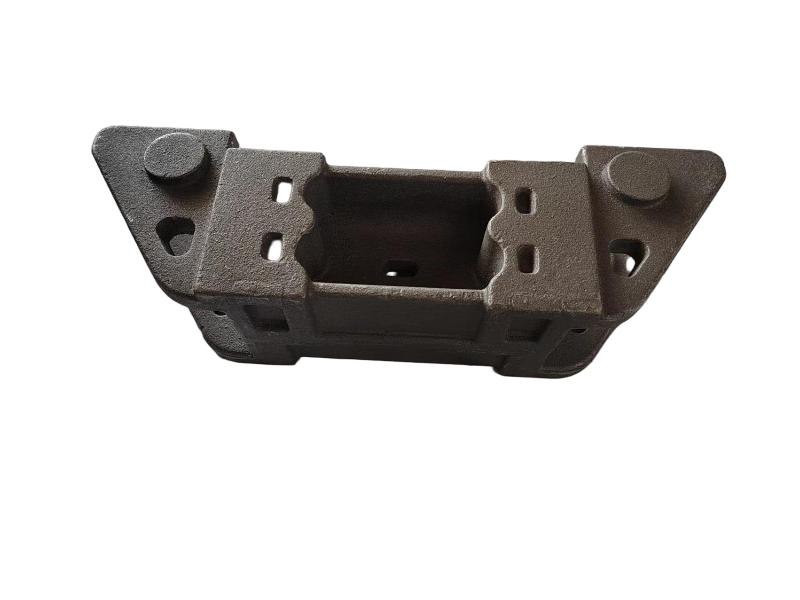
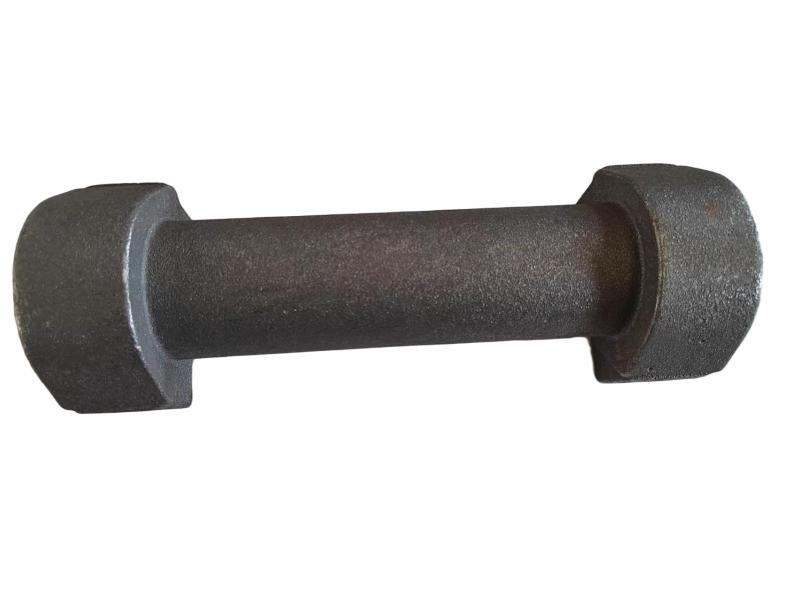
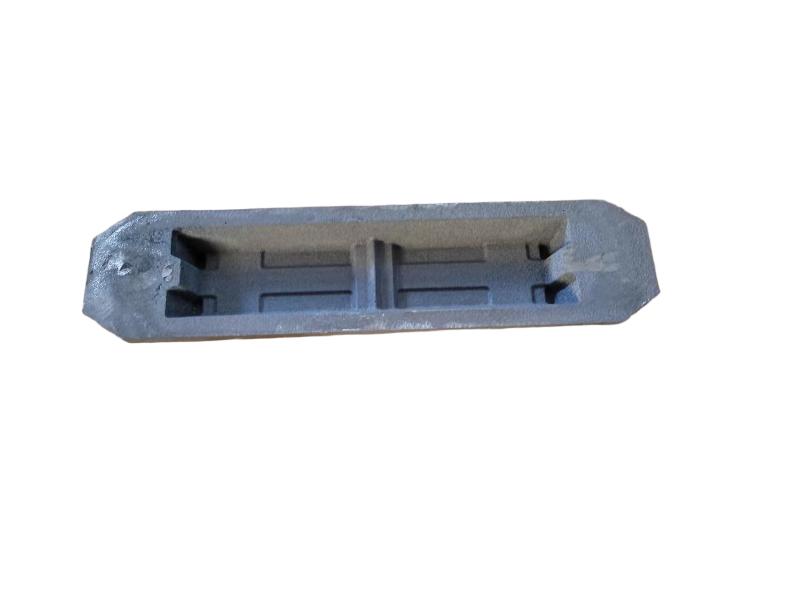
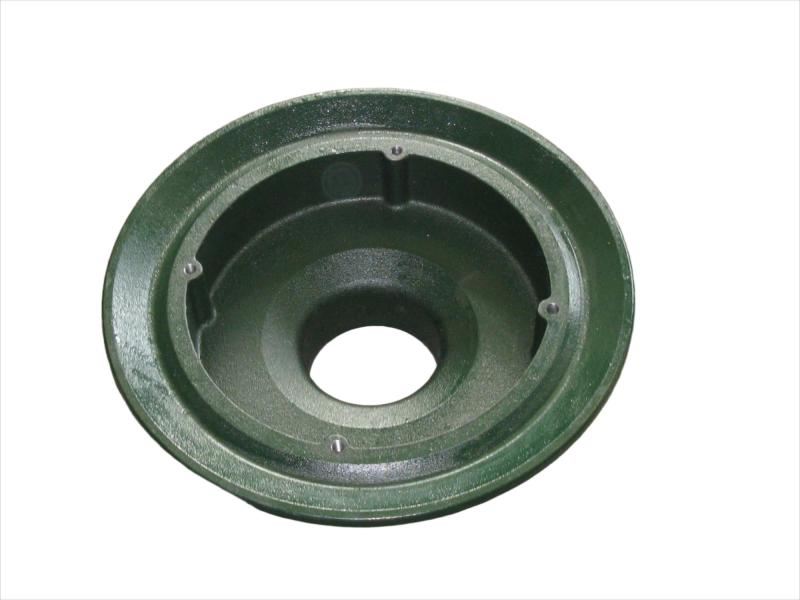
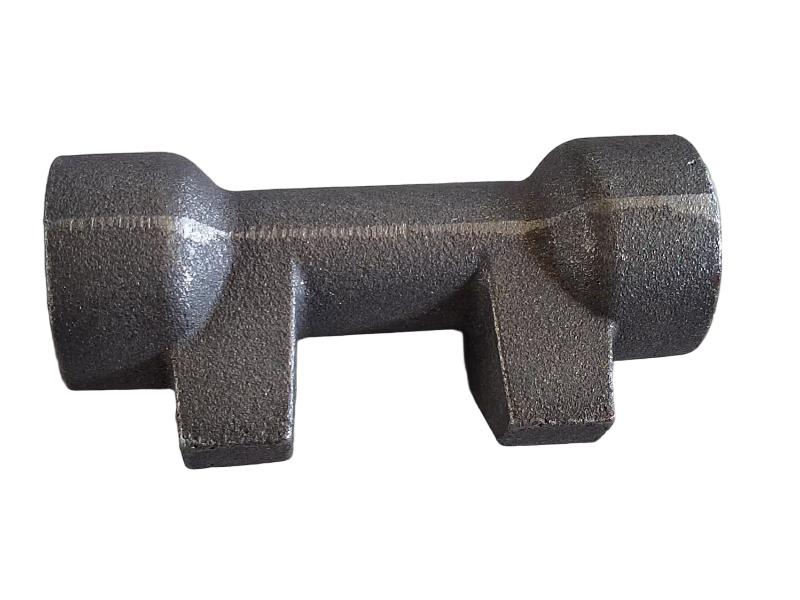
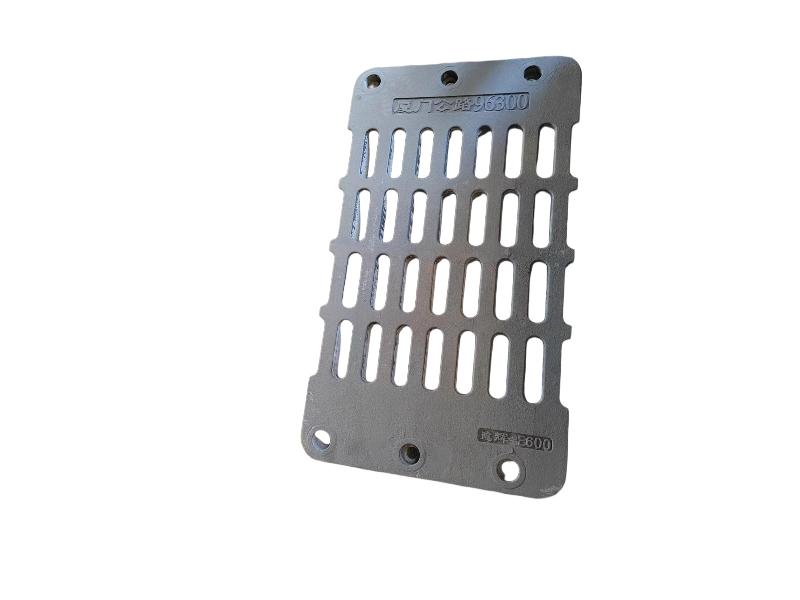
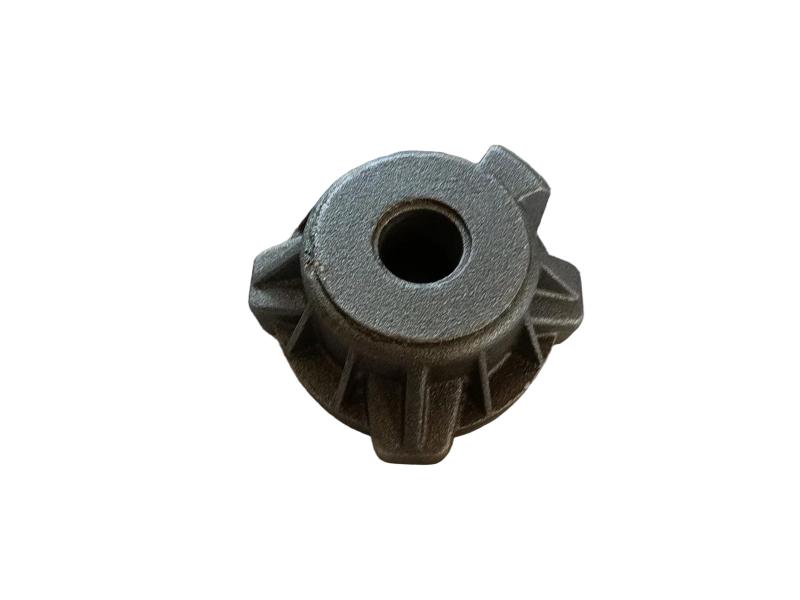
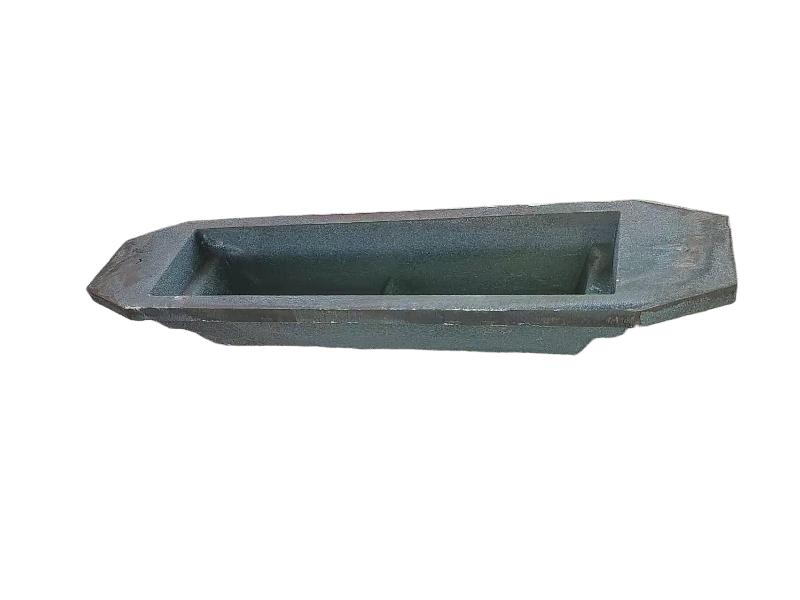
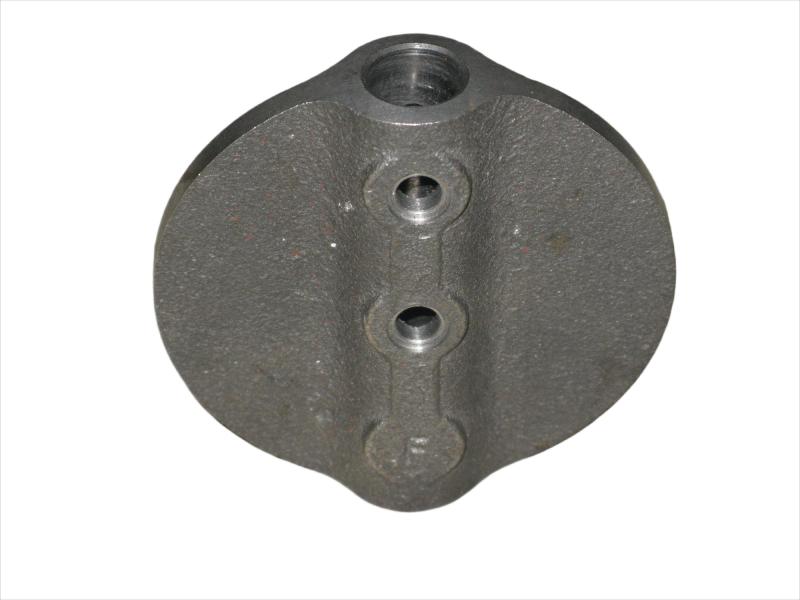
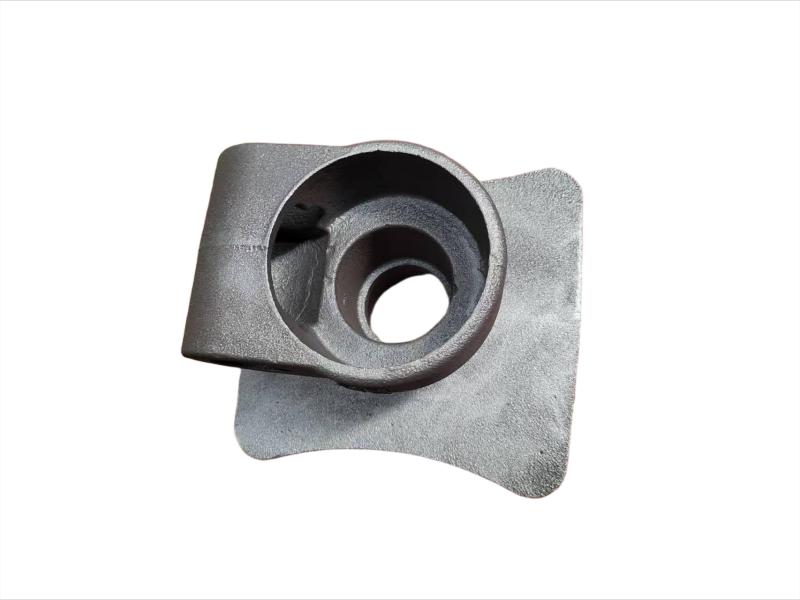
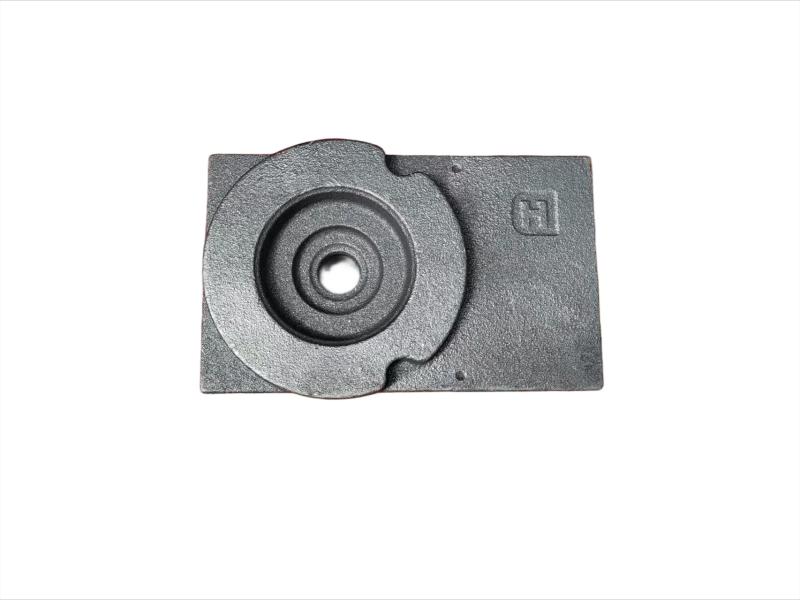
Wheel brake usually include many accessory , such as wheel brake frame, wheel brake lever, wheel brake spring cylinder, wheel brake position cylinder. Wheel brake frame is a structural component of a vehicle's braking system, specifically referring to the part that houses the brake components at each wheel. It provides a mounting point for the brake caliper (in disc brake systems) or the brake shoes (in drum brake systems) and connects to the wheel hub. Essentially, it's the framework that supports the braking mechanism at each individual wheel.
| Production Line Capabilities |
1.Vacuum Casting Line: Enables large-batch production and smooth surface medium parts

2.Resin Sand Casting Line: Delivers big complex geometries, but small quantity

3.Clay Sand Casting Line: Enables large-batch production small part and smooth surface medium parts

4.Medium-frequency Induction Furnace: Make sure uniform melting and stable quality

Comparative qualities of cast irons
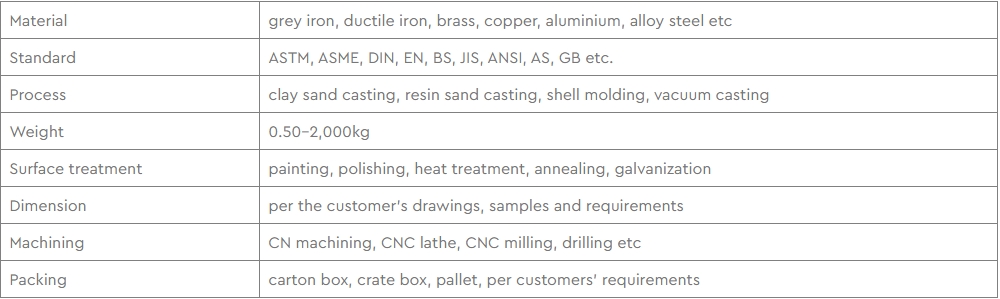
| Name |
Nominal composition [% by weight] |
Form and condition |
Yield strength [ksi (0.2% offset)] |
Tensile strength [ksi] |
Elongation [%] |
Hardness [Brinell scale] |
Uses |
| Grey cast iron (ASTM A48) |
C 3.4, Si 1.8, Mn 0.5 |
Cast |
— |
50 |
0.5 |
260 |
Engine cylinder blocks, flywheels, gear box cases, machine-tool bases |
| White cast iron |
C 3.4, Si 0.7, Mn 0.6 |
Cast (as cast) |
— |
25 |
0 |
450 |
Bearing surfaces |
| Malleable iron (ASTM A47) |
C 2.5, Si 1.0, Mn 0.55 |
Cast (annealed) |
33 |
52 |
12 |
130 |
Axle bearings, track wheels, automotive crankshafts |
| Ductile or nodular iron |
C 3.4, P 0.1, Mn 0.4, Ni 1.0, Mg 0.06 |
Cast |
53 |
70 |
18 |
170 |
Gears, camshafts, crankshafts |
| Ductile or nodular iron (ASTM A339) |
— |
Cast (quench tempered) |
108 |
135 |
5 |
310 |
— |
| Ni-hard type 2 |
C 2.7, Si 0.6, Mn 0.5, Ni 4.5, Cr 2.0 |
Sand-cast |
— |
55 |
— |
550 |
High strength applications |
| Ni-resist type 2 |
C 3.0, Si 2.0, Mn 1.0, Ni 20.0, Cr 2.5 |
Cast |
— |
27 |
2 |
140 |
Resistance to heat and corrosion |
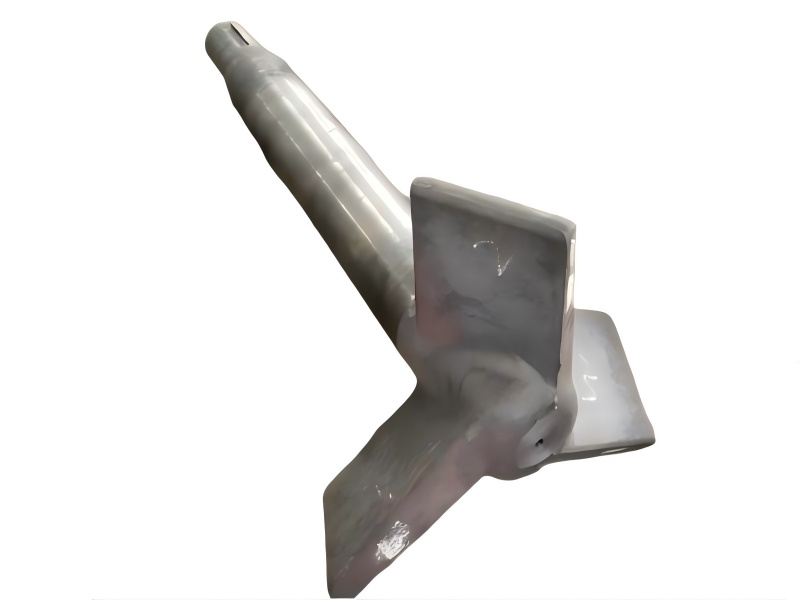










































 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported